Ever wondered how to keep your HVAC system running smoothly while saving water and energy? Air-cooled condensers are the answer. These units are designed to transfer heat efficiently without relying on a constant water supply, making them perfect for areas where water is scarce or expensive1. Whether you’re managing a commercial facility or upgrading your home system, understanding their design and maintenance can save you time and money.
Walk-In Cooler Guide: HVAC Installation & Optimization
Essential strategies for efficient refrigeration solutions
Ideal Temperature Range & Key Benefits
Optimal Temperature
Maintain temperature between 35°F to 41°F (2°C to 5°C) for perishable items
Key Benefits
- Extends product shelf life
- Ensures food safety compliance
- Reduces energy consumption
- Prevents product loss
- Maintains consistent quality
Maintenance Tips
- Clean evaporator coils annually
- Check door gaskets monthly
- Monitor humidity levels regularly
- Inspect insulation integrity
- Maintain proper airflow
Insulation Material Comparison
Key Installation Considerations
Location Selection
Insulation Quality
Refrigeration System
Regulatory Compliance
Prefabricated vs. Built-In Comparison
| Feature | Prefabricated | Built-In |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment |
| Customization | Limited options | Highly customizable |
| Installation Time | Quick setup | Longer installation period |
| Flexibility | Can be relocated | Permanent installation |
| Space Utilization | Standard sizes | Maximizes available space |
Energy Efficiency Factors
Frequently Asked Questions
Factors like surface area, fin type, and airflow rate significantly impact their heat transfer efficiency1. Regular cleaning and proper maintenance are essential to keep them performing at their best. This guide will walk you through everything from performance metrics to expert tips for upkeep.
Key Takeaways
- Air-cooled condensers save water and are ideal for dry regions.
- Heat transfer efficiency depends on design factors like fin type and airflow.
- Regular maintenance ensures peak performance and longevity.
- Energy-efficient technologies like VSDs reduce operational costs.
- Proper installation and spacing are crucial for optimal function.
Understanding the Basics of Air Cooled Condensers
Curious about how HVAC systems manage heat without water? An air-cooled condenser is the answer. This unit removes heat by transferring it to the surrounding air, making it ideal for areas where water is scarce or expensive2.
What is an Air Cooled Condenser?
An air-cooled condenser is a device that cools refrigerant gas by using ambient air. It’s a key part of your HVAC system, ensuring efficient heat transfer without relying on water. This makes it a cost-effective and eco-friendly solution3.
Inside the unit, refrigerant flows through coils while a fan blows air over them. This process removes heat, turning the gas into a liquid. The liquid refrigerant then moves to the evaporator, completing the cooling cycle4.
Key Functions in HVAC Systems
The primary role of an air-cooled condenser is to cool and condense refrigerant. It ensures your system operates efficiently, even in hot weather. Unlike water-cooled units, it doesn’t need a constant water supply, saving resources2.
Another advantage is its simplicity. With fewer components, it’s easier to install and maintain. This makes it a popular choice for both residential and commercial applications3.
By using ambient air, these units reduce energy consumption and operational costs. They’re also quieter than water-cooled systems, making them ideal for smaller spaces4.
Design Principles That Influence Performance
What makes some HVAC systems more efficient than others? It’s all in the design. The way your unit is built directly impacts its ability to transfer heat and maintain optimal cooling. Let’s break down the key design features that make a difference.
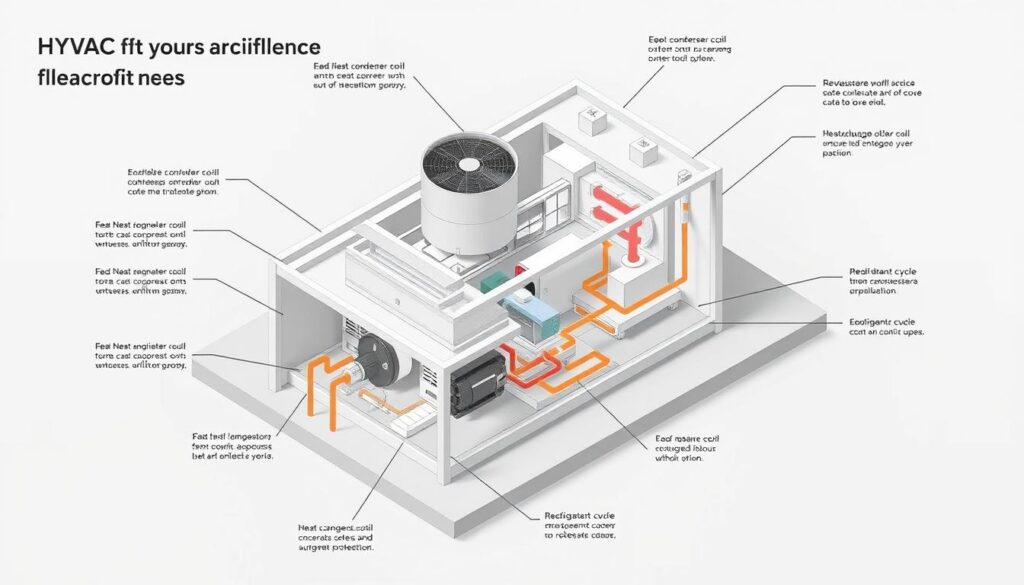
Heat Transfer Efficiency and Fin Design Considerations
Think of fins as nature’s radiator fins—they maximize heat transfer by increasing surface area. The design of these fins plays a critical role in how well your system performs. For example, helical fins with 7 to 11 fins per inch are commonly used for their efficiency4.
The surface area of coils also matters. Larger coils allow for better heat exchange, improving overall performance. Tubes with diameters ranging from 5/8 inch to 6 inches are often used, with 1 inch being the most common4.
Air Flow Dynamics and Cooling Performance
Airflow is the lifeblood of your system. Proper airflow ensures that heat is effectively removed from the refrigerant. The fan’s design and speed are crucial here. For example, fan speeds should not exceed 12,000 feet per minute to maintain mechanical integrity4.
The number of tube rows in a bundle also affects airflow. Typically, 4 to 10 rows are used to balance efficiency and control4. This ensures that the system can handle varying loads without compromising performance.
By focusing on these design principles, you can ensure your HVAC system runs efficiently and lasts longer. Look for units with well-designed fins, ample coil surface area, and optimized airflow for the best results.
Types of Air Cooled Condensers and Choosing the Right System
Choosing the right system for your HVAC setup can make all the difference in performance. Two popular configurations—forced draft and induced draft—offer unique advantages depending on your needs. Let’s break down the differences to help you make an informed decision.
Forced Draft versus Induced Draft Configurations
Forced draft systems use a fan to push air over the coil, ensuring efficient heat transfer. This setup is ideal for environments where consistent airflow is critical. It’s often preferred in industrial settings due to its robust performance under high pressure conditions5.
Induced draft systems, on the other hand, pull air through the unit. This design reduces the risk of recirculation, making it suitable for areas with limited space. It’s also quieter, which is a plus for residential applications6.
Which Configuration is Right for You?
Here are some factors to consider when choosing between forced draft and induced draft systems:
- Operating Conditions: Forced draft excels in high-pressure environments, while induced draft is better for space-constrained areas.
- Energy Use: Induced draft systems often consume less energy, making them a cost-effective choice for long-term use.
- Ambient Conditions: If you’re in a hot climate, forced draft may provide better cooling efficiency5.
Manufacturers recommend evaluating your specific cooling demands and environmental factors before making a decision. For example, if your system requires a Total Heat Rejection (THR) of 348,750 Btuh, a forced draft setup might be more suitable6.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your unique needs. Whether you prioritize performance, energy efficiency, or noise levels, understanding these configurations will help you select the best system for your setup.
Air cooled condenser guide: Performance Metrics and Efficiency
Want to know how to maximize your HVAC system’s efficiency without breaking the bank? Understanding performance metrics and optimizing refrigerant flow are key to achieving this goal. Let’s dive into the technical details in a way that’s easy to grasp.
Optimizing Refrigerant and Temperature Control
How do you measure your system’s efficiency? Metrics like Total Heat Rejection (THR) and Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) are crucial. For example, higher EER values indicate better efficiency, with some units achieving up to 95% under optimal conditions7.
Controlling temperature is equally important. Proper refrigerant flow ensures your system operates smoothly. Studies show that modern control strategies can improve efficiency by 15-25%7. This reduces the workload on your compressor, saving energy and costs.
Here are some actionable tips to optimize your system:
- Monitor THR and EER: Regularly check these metrics to ensure your unit is performing at its best.
- Adjust Fan Speed: Optimal fan speeds can improve efficiency by up to 18%7.
- Clean Coils: Dirty coils can reduce performance by up to 10%, so keep them clean8.
Balancing energy savings and cost considerations is essential. For instance, using sustainable refrigerants like HFCs can reduce environmental impact while maintaining efficiency9. By following these strategies, you can ensure your system runs efficiently and lasts longer.
Operational Mechanics and Temperature Control Methods
Have you ever wondered how your HVAC system keeps your space comfortable while managing heat efficiently? The secret lies in the refrigerant cycle and advanced temperature control methods. Let’s break it down so you can understand how it all works.
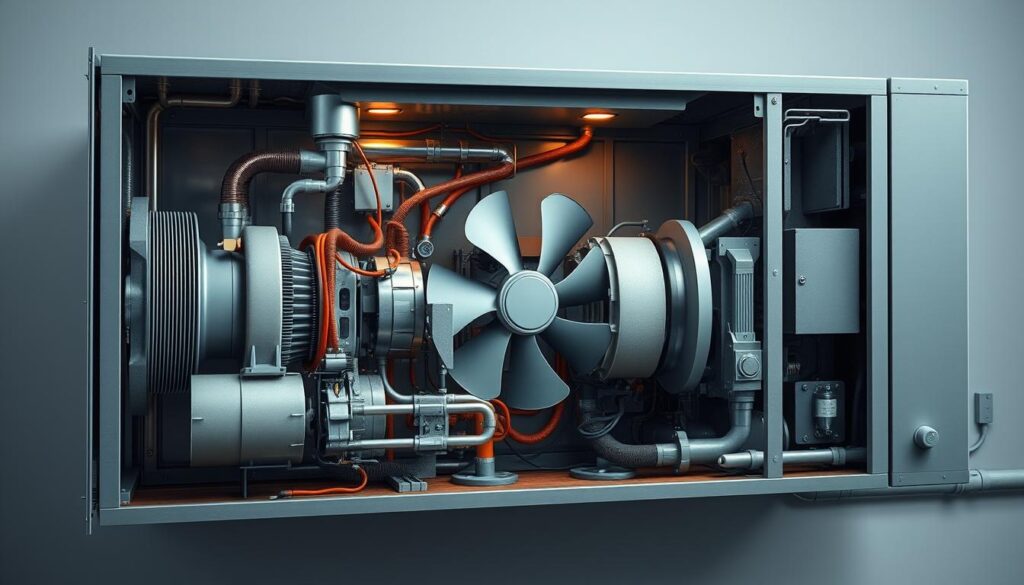
The Refrigerant Cycle Explained
The refrigerant cycle is the heart of your HVAC system. It starts when the compressor pumps refrigerant gas into the condenser. Here, the gas releases heat and turns into a liquid. This liquid then flows to the evaporator, where it absorbs heat from your space and turns back into a gas10.
This cycle repeats continuously to maintain your desired temperature. Think of it like a relay race—each component passes the baton (heat) to the next, ensuring your space stays cool11.
Thermostatic and Fan Control Strategies
Controlling temperature isn’t just about the refrigerant—it’s also about how the fan operates. Thermostatic controls adjust the fan speed based on the cooling demand. For example, slower speeds save energy during mild weather, while faster speeds provide maximum cooling on hot days11.
Here’s a quick comparison of fan control strategies:
| Strategy | Benefit | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Fan Speed | Energy-efficient | Mild weather |
| Fast Fan Speed | Maximum cooling | Hot weather |
| Variable Speed | Balanced performance | All conditions |
By optimizing these controls, you can balance comfort and energy efficiency. For instance, maintaining a fan speed that doesn’t exceed 12,000 feet per minute ensures both performance and durability11.
Remember, a well-maintained system not only keeps you comfortable but also saves you money in the long run. Regular checks and adjustments are key to ensuring everything runs smoothly.
Material Selection and Installation Best Practices
Looking to boost your HVAC system’s durability and efficiency? The right materials and installation practices can make all the difference. Choosing corrosion-resistant materials and ensuring proper siting can extend your system’s lifespan and improve performance.

Corrosion Resistance and Thermal Conductivity Considerations
When selecting materials, focus on corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. Stainless steel, aluminum, and copper are popular choices. Stainless steel offers excellent durability, while aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective. Copper provides superior thermal conductivity, making it ideal for heat transfer12.
Here’s a quick comparison of these materials:
| Material | Corrosion Resistance | Thermal Conductivity | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High | Moderate | Harsh environments |
| Aluminum | Moderate | High | Cost-sensitive projects |
| Copper | High | Very High | Efficient heat transfer |
Proper material selection ensures your system performs well in various conditions. For example, stainless steel is ideal for coastal areas where salt exposure is high13.
Siting, Space Requirements, and Environmental Impact
Installation location is just as important as material choice. Ensure your unit is placed at least four feet from walls or obstructions to allow proper airflow12. For multiple units, maintain a distance equal to the width of the largest unit to prevent recirculation12.
Consider environmental factors like noise and solar gain. Decorative fences around units should have at least 50% free area and a one-foot undercut to ensure airflow12. Proper siting reduces energy consumption and minimizes environmental impact14.
By following these best practices, you can enhance your system’s efficiency and longevity. Investing in quality materials and thoughtful installation pays off in the long run.
Maintenance, Servicing, and Troubleshooting Tips
Keeping your HVAC system in top shape doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With a few simple steps, you can ensure your condenser runs efficiently and lasts longer. Regular maintenance not only improves performance but also saves you money in the long run15.

Effective Cleaning Procedures and Wear Monitoring
Cleaning your condenser is one of the most effective ways to maintain its efficiency. Dirty coils can reduce airflow by up to 50%, impacting cooling performance16. Here’s how to keep your unit clean:
- Clean Coils Regularly: Outdoor coils can collect dirt, especially in dusty environments. Cleaning them once or twice a year can prevent a 30% drop in efficiency15.
- Inspect Fins: Bent fins can block airflow, reducing efficiency by up to 20%. Straighten them carefully using a fin comb16.
- Check Filters: Replace or clean filters every 1-3 months to maintain optimal airflow and prevent coil freezing15.
Monitoring wear on key components like the fan and motor is equally important. Regular inspections can help you spot issues early and avoid costly repairs17.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with regular maintenance, issues can arise. Here are some common problems and how to address them:
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Warm Air | Clogged coils or low refrigerant | Clean coils or call a professional to check refrigerant levels17. |
| Reduced Airflow | Dirty filters or bent fins | Replace filters or straighten fins16. |
| Water Leaks | Clogged condensate drain | Clear the drain to prevent equipment shutdown16. |
Proactive maintenance can extend your system’s lifespan by 5 to 10 years15. By following these tips, you’ll keep your condenser running smoothly and efficiently.
Innovations and Future Outlook in HVAC Condenser Technology
What’s next for HVAC technology? The future is here, and it’s smarter, greener, and more efficient than ever. From smart control systems to groundbreaking research, the industry is evolving rapidly to meet modern demands. Let’s explore the latest advancements and what they mean for your system.
Smart Control Systems and Energy Saving Technologies
Smart HVAC systems are transforming how we manage temperature and energy use. By integrating IoT devices, these systems offer real-time monitoring and control, reducing energy consumption by up to 30%18. For example, Johnson Controls’ OpenBlue platform uses AI to predict maintenance needs, cutting unexpected downtime by 66%19.
Variable speed drives (VSDs) are another game-changer. They adjust fan speeds based on demand, improving efficiency and lowering costs. Modern condensers with larger coils and fans also enhance heat transfer, making them more effective than older models20.
Emerging Trends and Research Directions
The shift toward eco-friendly refrigerants like R-32 and R-454B is gaining momentum. These alternatives have a lower environmental impact and better energy performance18. Research is also focusing on microchannel technology, which improves heat exchange and reduces material use.
Predictive maintenance powered by AI is another exciting trend. It helps identify potential issues before they become costly problems, saving up to 20% in maintenance expenses18. Remote monitoring systems are also becoming standard, allowing users to manage their unit from anywhere.
Here’s a quick look at what’s shaping the future:
- Smart Controls: IoT and AI for real-time efficiency.
- Eco-Friendly Refrigerants: Lower environmental impact.
- Microchannel Technology: Enhanced heat transfer.
- Predictive Maintenance: Proactive problem-solving.
By staying informed about these innovations, you can plan upgrades that boost performance and sustainability. The future of HVAC is bright, and it’s time to embrace it.
Final Thoughts on Your Air Cooled Condenser Journey
Ready to take your HVAC system to the next level? By now, you’ve learned how design, operation, and maintenance play a crucial role in optimizing performance. Whether it’s choosing the right refrigerant or ensuring proper airflow, every detail matters21.
Start by assessing your current unit. Look for signs of wear, clean the coils, and check the fan for optimal performance. Regular maintenance can extend your system’s lifespan and improve efficiency22.
Don’t hesitate to consult manufacturers for tailored solutions. They can help you leverage innovations like smart controls and eco-friendly refrigerants to boost energy savings23.
Finally, stay curious. The HVAC industry is evolving, and staying informed ensures your system remains efficient and reliable. With these insights, you’re ready to transform technical knowledge into everyday confidence.
FAQ
What is an air-cooled condenser?
How does an air-cooled condenser improve HVAC performance?
What are the differences between forced draft and induced draft configurations?
How can I optimize refrigerant and temperature control in my system?
What materials are best for air-cooled condensers?
What maintenance practices extend the life of an air-cooled condenser?
Are there energy-saving technologies for air-cooled condensers?
What should I consider when installing an air-cooled condenser?
Source Links
- Air Cooled Condenser: A Comprehensive Guide
- Wine Cellar Refrigeration Systems
- AC Condenser Unit: Everything You Need to Know
- Layout 1
- How to Choose The Right Air-cooled Condenser
- Choosing the Right Air-Cooled Condenser
- Performance Assessment of Air-Cooled Steam Condenser with Guide Vane Cascade – Journal of Thermal Science
- Getting top performance from your air-cooled condenser
- Air Cooled Condenser Chiller: A Comprehensive Guide
- Microsoft Word – ACC inspection guidelines 05.12.2015 Initial Version.doc
- Measure Guideline: Evaporative Condensers
- HVAC Quality Installation Specification (ACCA Standard 5)
- The DIY AC Maintenance Guide: Maximize Your AC Performance
- Air Conditioner Maintenance
- GUIDE: HVAC Condenser Problems & How To Avoid Them | Spurk HVAC
- HVAC Tech for 2025: Trends, Skills & Future Opportunities
- Innovations maintaining the air quality in HVAC systems – GreyB
- Unpacking the Size: Why Modern AC Condensers are Bigger & Efficient
- Vol 8 Fundamentals – Part 8 Air Cooled Condensers
- ACC Leak/Performance Issue – Air-Cooled Condenser Users Group
- AIR-COOLED CONDENSERS: Chemistry, corrosion, performance, O&M dominate annual user-group program




0 Comments